

- #WHY CAN YOU US H2 PDC TO REMOVE BENZYL ESTER MANUAL#
- #WHY CAN YOU US H2 PDC TO REMOVE BENZYL ESTER CODE#
Q: On slide 443: why does DMT-Cl react w/ the 5'-OH and not the 3'-OH?Ī: For the same reasons as above. Q: Why is chemical DNA synthesis done 3' to 5'?Ī: The primary 5'-hydroxy group is less hindered and therefore more nucleophilic than the secondary 3'-hydroxy group. Be sure to remember that the chemical synthesis of DNA and peptides is done in the opposite deirection as the convention for writing a sequence. I believe they actually made 3'-CTAG-5'.Ī: You are correct.
#WHY CAN YOU US H2 PDC TO REMOVE BENZYL ESTER MANUAL#
Q: I believe that the solutions manual made a mistake in synthesizing 5'-CTAG- 3' (Problem 28.49).
#WHY CAN YOU US H2 PDC TO REMOVE BENZYL ESTER CODE#
Q: On slide 369 we have a heading for section 26.9 with the (please read) caption, which we really know is secret code for "you will not be tested on this." Slide 370-377 then seem to fit under this heading.

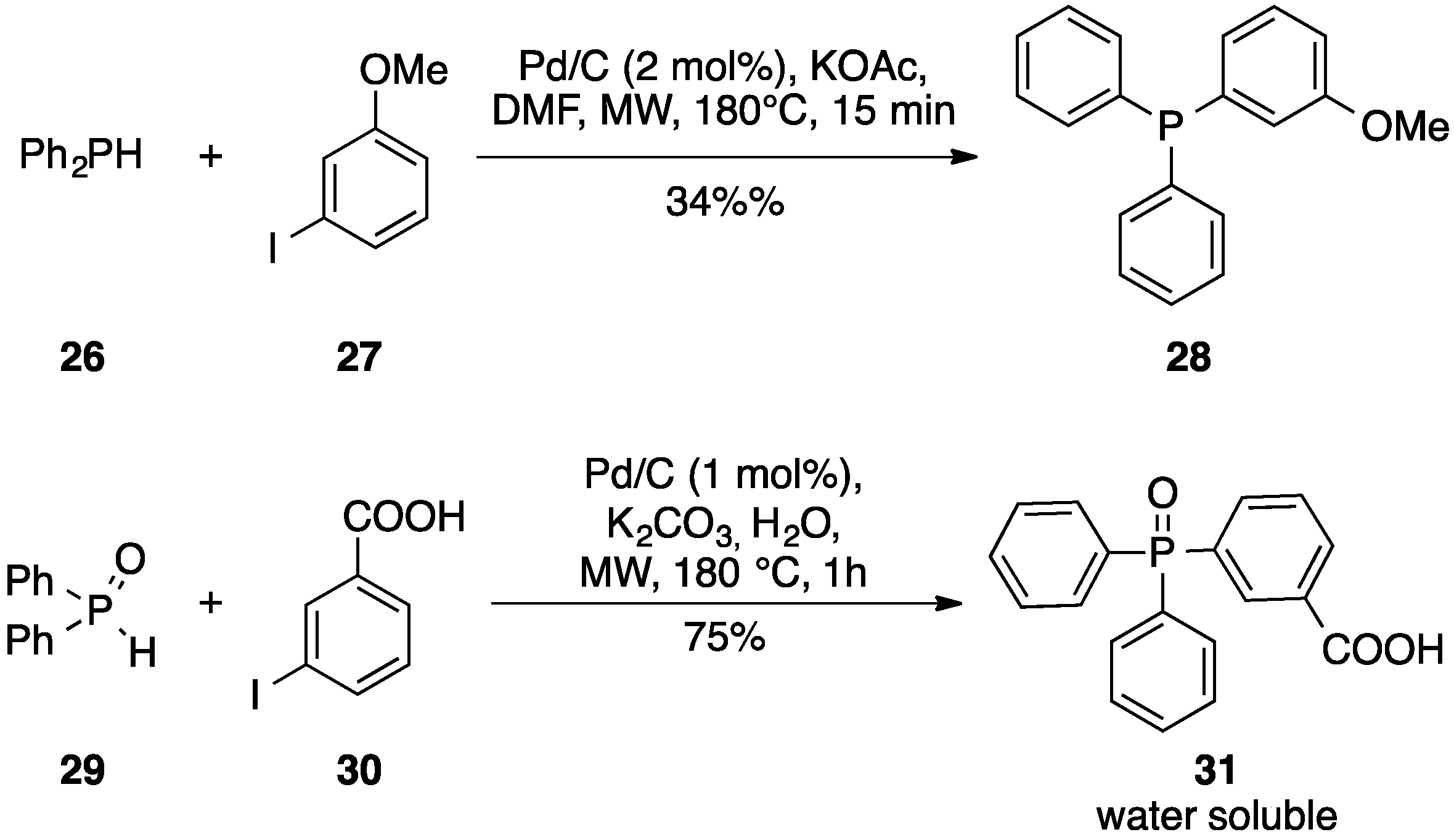
Q: I was also unsure as to whether or not specific structure knowledge for portions of chapter 27 (i.e., phospholipids, prostaglandin, etc) would fall under the same category as the amino acid table.Ī: As with the amino acids, you do not need to know specific structures, but you should be able to identify specific classes of compounds. Q: Just to clarify, we do not need to know the amino chart in the beginning of chapter 26, right?Ī: You do not need to know the structures amino acids per se (by popular demand), but you should be able to identify a hydrophobic, hydrophilic, basic and acidic amino acid when you see one. Q: Will you be offering the alternate final exam on Wednesday, May, 3rd?Ī: As stated on the syllabus, there will be no alternative final exam offered. So the themes may be represented more so than the individual chapters.

Themes somtimes reappear in subsequent chapters with expanded scope or emphasis (amine synthesis and amino acid synthesis). There are overlapping themes in many of the chapters, i.e., Chapters 15 - 16 and part of 24 (electrophilic substitution), and chapters 19-23 (carbonyl chemistry). My intent is that all the chapters will be equally represented on the final. In contrast with past interpretations, an electrochemical approach is used to explain negative values for the Hammett reaction constant.Q: Will the Final exam emphasize the chapters 26-28 or will it also be more of a comprehensive final?Ī: It will be comprehensive. At a molecular level the oxidative, rate-determining step is suggested to be triggered by the retraction or shrinkage of electron pairs from sigma bonds in Cr 2 VI species to non-bonding orbitals in unstable Cr IV–O–Cr VI Modelling of parameter λ in terms of the electrostatic theory showed its experimental value to be consistent with the ratio of electric potentials generated in the immediate vicinity of the nearest chromium atom by dipolar substituents introduced in the aromatic ring on para and meta positions. A mechanism implicating the prior acid-catalysed formation of neutral benzyl hydrogen dichromate ester followed by intramolecular proton transfer is proposed. = 1.09 ± 0.05 for the para/ meta ratio of inductive or Electra effects is obtained and negative Hammett reaction constants decreasing in magnitude with increasing temperature are found. Using the tetralinear approach to substituent effects, For ortho-substituted benzyl alcohols high Δ ‡ H° values and small negative Δ ‡ S° values point to an ortho effect on the rate-determining step. From good linear Eyring plots activation enthalpies Δ ‡ H° and entropies Δ ‡ S° are calculated. Benzaldehyde is the only oxidation product and no reaction takes place without TCA. The kinetics were followed spectrophotometrically in dry acetonitrile acidified with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) using pyridinium dichromate (PDC) as oxidising agent under pseudo-first-order conditions with respect to PDC. Rate constants were measured for the oxidation reaction of benzyl alcohol and twenty-five ortho-, meta- and para-monosubstituted derivatives in the temperature range 293–323 K at intervals of 10 K.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
